Have you ever wondered what makes a leader truly effective?
Recent research has shed light on this topic, suggesting that there are four key behaviors that can make a difference 1. These behaviors, when cultivated, can transform individuals into leaders who not only excel in their roles but also inspire and elevate those around them and an entire organisation.
1. Solving Problems Effectively
In a research paper published in the International Journal of Indian Psychology, quick and efficient decision making is a key characteristic of a good leader (Wesley & Narayan, 2023). They have the ability to understand complex situations, identify key issues, and come up with solutions that address these issues; this requires both analytical thinking and creativity.
Several studies also highlight that effective problem-solving is a critical component of successful leadership 2. According to Charles Kerns, PhD, a leader’s competence in decisively solving problems helps drive leadership effectiveness and organisational success.3
Additionally, McKinsey’s research on leadership underscores the importance of problem-solving capabilities. Effective leaders are noted for their ability to adapt their strategies to the specific context and stage of their organisation’s development. This involves a keen ability to navigate problems and implement solutions that align with long-term organisational goals (McKinsey & Company).
2. Operating with a Strong Results Orientation
McKinsey’s extensive research into leadership effectiveness highlights that operating with a strong results orientation is crucial for leadership success. This characteristic involves leaders emphasizing efficiency, productivity, and prioritizing high-value work to achieve set goals.
Leadership is not just about having a vision—it’s about making that vision a reality.
3. Seeking Different Perspectives
An article published in the Strategic Management Journal examines the role of cognitive flexibility in strategic leadership and underscores the significance of seeking different perspectives to navigate complex business environments 4 .
Seeking different perspectives is a conspicuous trait in managers who monitor trends affecting organisations, grasp changes in the environment, encourage employees to contribute ideas that could improve performance, accurately differentiate between important and unimportant issues, and give the appropriate weight to stakeholder concerns (Feser, Mayol, Srinivasan, 2015).
The best leaders understand that they don’t have all the answers. They value diversity of thought and are open to different perspectives. By seeking input from others, they are able to make more informed decisions. This behavior also fosters a culture of inclusivity and collaboration, where everyone feels valued and heard.
4. Supporting Others
Effective leaders are those who support others. They are empathetic and understanding, always ready to lend a hand when needed. They foster a positive environment where their team members feel supported and motivated to do their best.
If the leader is supportive, coaching-oriented, and has non-defensive responses to questions and challenges, members are likely to conclude that the team constitutes a safe environment. In contrast, if team leaders act in authoritarian or punitive ways, team members may be reluctant to engage in the interpersonal risk involved in learning behaviors such as discussing errors 5 . By showing genuine care for their team, these leaders build trust and loyalty.
Did You Know?
Did you know the Health and Safety Dx diagnostic is designed to evaluate core aspects of safety leadership, engagement, systems and health & wellbeing. Results are also represented as seven Dimensions to focus on both conditions and behaviours that support high performance.
Six of these seven Dimensions represent typical leadership behaviours many organisations strive to promote – refer to digram 1.1 below. Interestingly, several of these Dimensions also align with the above-mentioned leadership behaviours, i.e.,
- Courageous Decisions: “Problem Solving”, effectice decision making and standing up for what is right are great leadership attributes.
- Executing with Excellence: “Operating with a strong results orientation” includes the ability to get stuff done!
- Recognise & Respond: “Seeking Different Perspectives” often includes seeking feedback, self-reflection and demonstrating a positive response.
- Demonstrating Care & Concern: Aligns with the concepts of “Supprting Others”, can include putting yourself in someone else’s shoes, demonstrating empathy and compassion to genuinely connect and care for others.
- Clear Expectations: Often refers to the perceived clarity in communicating direction or tasks as received, observed, and understood. For more information on setting expectations, refer to our blog “The Painful Impact of Unclear Expectations”
- Collaborate & Enable: Stakeholders ability to work effectively together to build effective capacity and capability.
- Conditions & Experience: Although the seven Dimension is not specially designed as a leadership behaviour, creating a safe workplace environment, with tools, plant and equipment that are fit-for-purpose and user friendly are foundations for build a great culture.
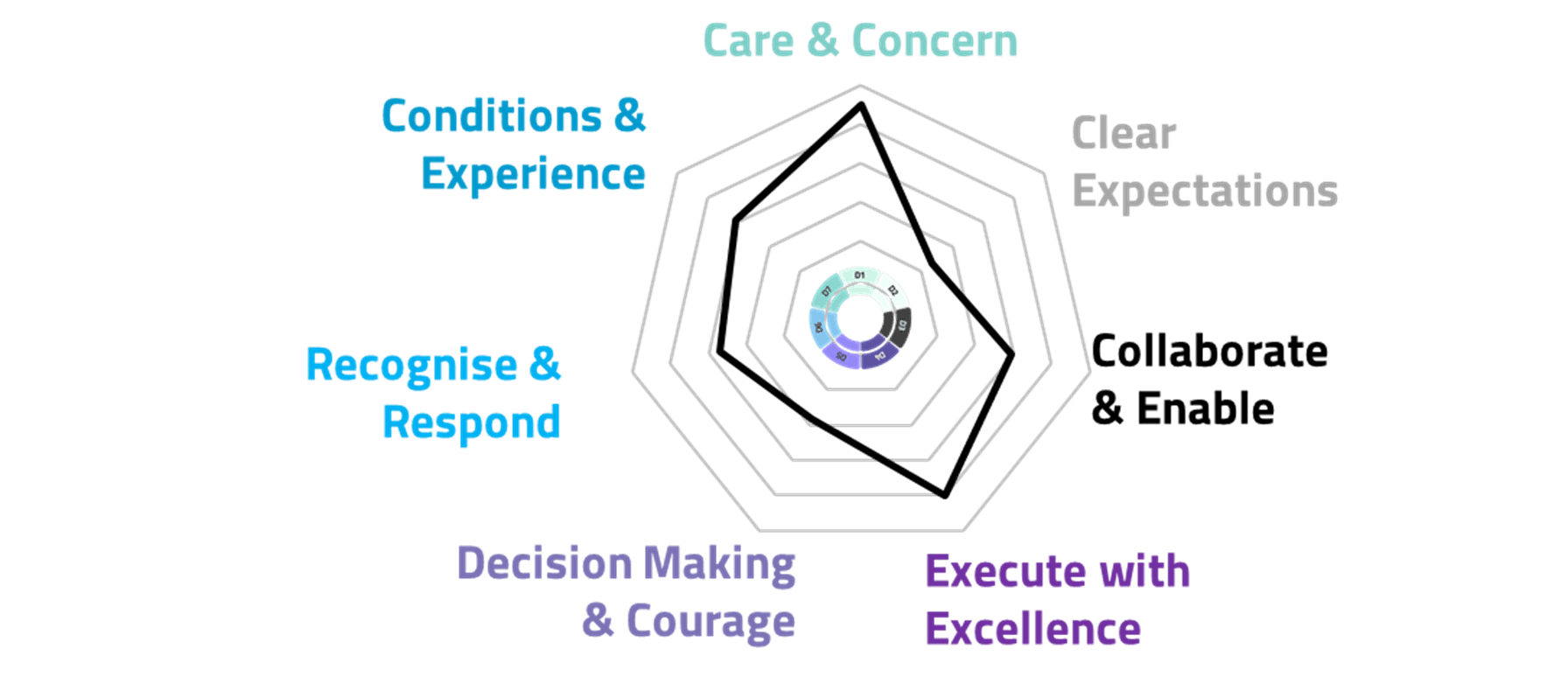
Figure 1.1 Health and Safety Dx Dimensions
Conclusion
Although the above-mentioned research shortlists four specific behaviours, its important to acknowledge that effective leaderhip is often situational based on your own capability, style and the needs of your operating environment. Self-reflecting on your own values, belief and behaviors, can provide opportunities to create a positive impact with relevant stakeholders, teams, organisations.
Reflect on your own leadership and take a free sample safety leadership self-assessment today – click here.
References:
- Feser, Mayol, Srinivasan. (2015). Decoding leadership: What really matters. McKinsey Quarterly. ↩︎
- Kurec, A. (2016). Follow the Leader: Developing Great Leadership Skills. Critical Values. ↩︎
- Kerns, C. D. (2016). Decisive Problem Solving: A Key Leadership Practic. Journal of Management Policy and Practice Vol. 17(2). ↩︎
- Brusoni, D. L.-M. (2017). Cognitive flexibility and adaptive decision-making: Strategic Management Journal. ↩︎
- Edmondson, A. (1999). Psychological Safety and Learning Behavior in Work Teams. Administrative Science Quarterly. ↩︎
